You should enable the Add date and time from the text message and Add number from the text message
options. In this case, the program will add the corresponding data to the message text and pass it for further
processing and inserting SMS to database.
You should enable the Query modemoption if the modem cannot notify the computer about new incoming
text messages. In this case, the program will query the modem for new messages every 10 seconds.
Notifications are configured with the help of the AT+CNMI modem initialization string and it is specific for each
modem model. You should consult the manual for the AT commands of your modem. The ” SMS GSM modem settings and configuration” section contains sample commands
for some modem types and the more detailed descriptions of other options.
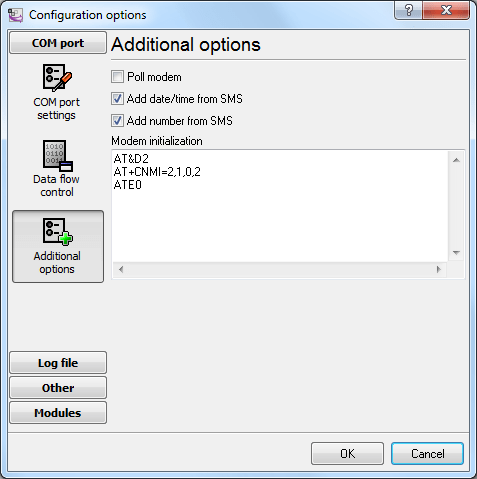
Fig. 1. Advanced modem options
After receiving a text message, the incoming text message module passes it to the parser for processing. The parser
splits the incoming text message into several separate values. When a text message is received, it looks in the main
window of the program like this:
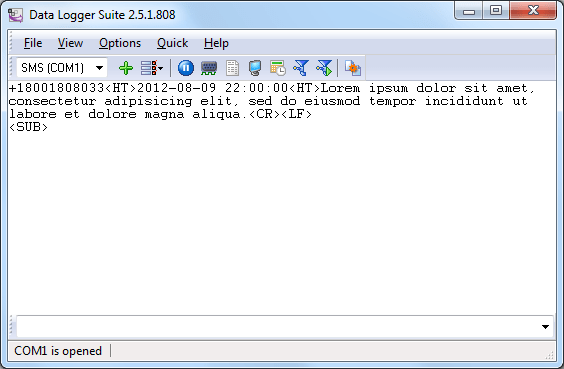
Fig. 2. Main window
NUMBER<HT>DATE and TIME<HT>MESSAGE TEXT<CR><LF><SUB>
<HT> – the ASCII tabulation character with the hexadecimal code of 0x09h <CR> – the ASCII carriage return
character with the hexadecimal code of 0x0Dh <LF> – the ASCII new line character with the hexadecimal code of
0x0Ah <SUB> – the ASCII file end character with the hexadecimal code of 0x1Ah
If you disable either the Add data and time from the text message option or the Add number
from the text messageoption, the data packet will look like this:
NUMBER<HT> MESSAGE TEXT<CR><LF><SUB>
or
DATE and TIME<HT>MESSAGE TEXT<CR><LF><SUB>
You should use the “ASCII Data Parser” module included in the installation package as your parser. You should enable
this parser on the Query Analysis Filteringtab (fig. 1).
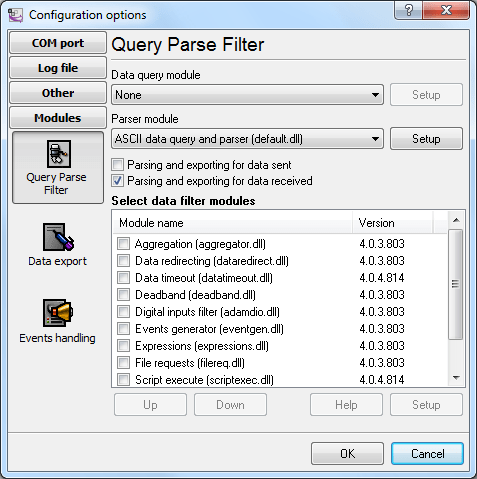
Fig. 3. Selecting the parser
Then you should open the parser configuration dialog box (fig. 4) using the Setupbutton.
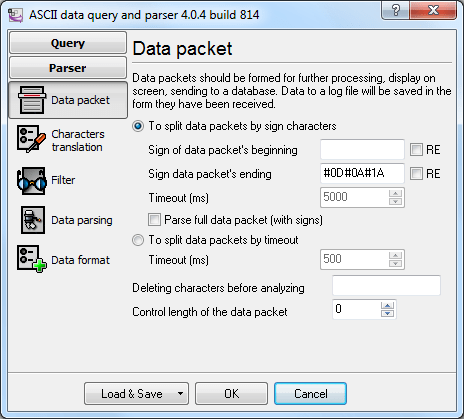
Fig. 4. Specifying the data packet properties
Split packets by the start/end signs – enabled. Specify the #0D#0A#1A in the Packet End
Signfield, which corresponds to the hexadecimal codes of the following ASCII characters: <CR>,
<LF> and <SUB>.
If necessary, you can configure a filter that will filter out unneeded text messages. You can find detailed
information about this feature in the help file.
You should specify the fields a text message contains on the Data Parsingtab (fig. 5).
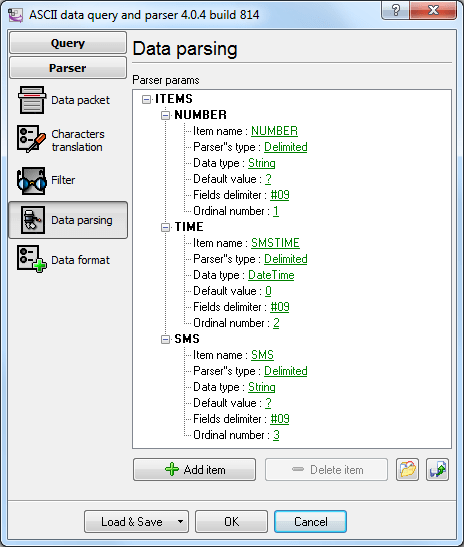
Fig. 5. Configuring the data packet format
You should add the description of all values you want to extract from a text message to the tree with parser items.
Figure 5 shows the settings for a data packet that is generated when the Add date and time from the text
message and Add number from the text messageoptions are enabled.
You should specify the format of date and time extracted from a text message in the Date and Time
field on the Data Formattab (fig. 6). The program always uses the ISO format YYYY-MM-DD HH:NN:SS. The
date and time string will be converted into a value of the Datetime type with the help of this format. If the format
is specified incorrectly, the program will display the corresponding error message. You can find the detailed
description of the characters that can be used in the date and time format in the help file.
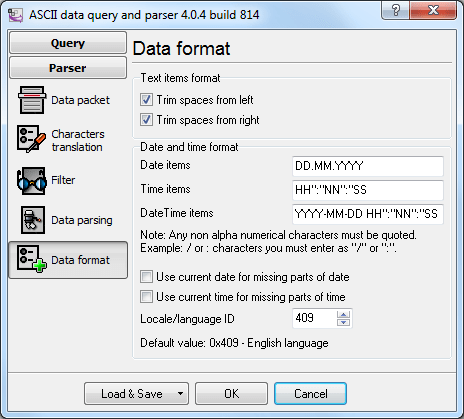
Fig. 6. Date and time format
You should test the parser after you configure it.
1. To do it, click the OKbutton to save the changes.
2. Enable the DDE Server data export module (fig. 7)
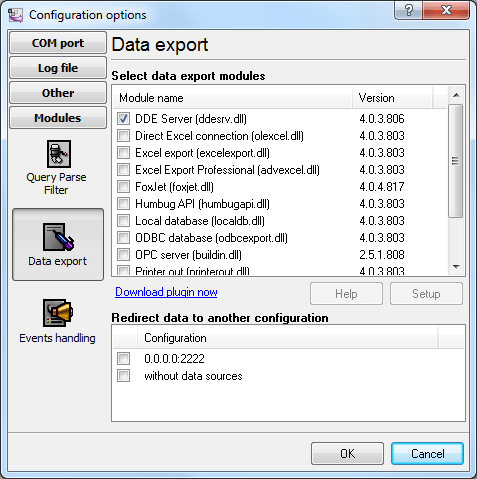
Fig.7. Data export module
3. Click the OKbutton to save the changes.
4. Wait for a new incoming text message to appear in the main window of the program.
5. Open the configuration dialog box and double-click the DDE Server data export module. Switch to the All
active itemstab in the DDE Server dialog box (fig. 8). This list must contain the configured parser items
and their values. Here you can check whether the parser is configured correctly and, if necessary, make changes in its
configuration.
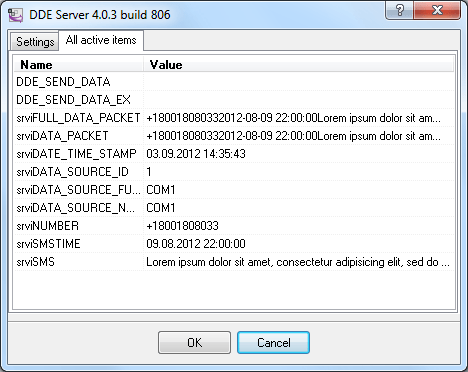
Fig. 8. Active items
The parser also adds some additional items:
DATA_SOURCE_NAME – the number of the COM port used by the modem that received the message. If the program works with
several modems simultaneously, this item makes it possible to identify the modem.
DATA_TIME_STAMP – the date and time when the program processed the message. It may differ from the SMSTIME time.