Latest version:5.0.1 build 1205.December 12, 2025.
The JSON Data Parser plugin is designed for technical professionals who need to extract structured JSON data from a continuous data flow and make it available as parser variables for further processing. The plugin works together with Equvera CoNNeX TCP/IP Data Logger, Equvera CoNNeX Data Logger Suite, and Data Logger Suite. It reads JSON fragments from an incoming stream, parses them according to user rules, and exports selected values as typed parser items. These items can then be used in data export plugins to transfer data to SQL databases , files, Excel, CSV, or other destinations.
Some common uses are reading JSON messages from HTTP-based APIs over TCP, MQTT topics , or log files that are formatted in JSON. For instance, you can accept HTTP POST requests that contain JSON sensor measurements, or consume MQTT topics with device status updates. The plugin extracts the JSON content from any surrounding unnecessary bytes and creates internal variables such as, for example, temperature , device_id , or STATUS. This approach makes it easier to build reliable automation, control or logging solutions for important values.
The plugin focuses on three main tasks. First, it detects and extracts JSON structures from mixed data streams that may contain headers, delimiters, or other content. Second, it parses and filters JSON objects based on user-defined rules, including root object selection, name-based filtering, and maximum depth. Third, it converts the parsed values into specific data types and exports them as parser items that can be used in standard export plugins. This data processing method helps to normalize complex incoming JSON payloads and present them as a flat set of usable values.
JSON data can arrive from several sources. With Equvera CoNNeX TCP/IP Data Logger, it often comes from HTTP servers, REST services, or custom TCP services. With Data Logger Suite, it can come from MQTT brokers, text log files, or combined sources. Whatever channel the data comes in through, the JSON Data Parser plugin always handles it the same way. The JSON data and JSON valuestabs let you set the rules. The parser variables you create can then be used in all available data filter and export plugins.
At the center of the configuration is the Root object name setting. This is a case insensitive name of the JSON node that contains all values that you want to export. For example, if you specify RootNode , the plugin will scan each JSON structure for an object named RootNodeand will export only its properties and nested objects. This is useful when the incoming JSON contains multiple top level objects or includes diagnostic or metadata sections that you do not want to process.
Consider the following incoming JSON fragment inside a common data flow:
{ "root1":{ "id":2, "int":123, "float":321.01 }, "root2":{ "id":2 } }
If you set Root object name to root1 , the plugin will parse and export only the values under root1 . That means that properties id , int , and float will become parser variables, while the root2object will be ignored. It’s possible for the plugin to export values from all top-level objects it finds if you leave the root object blank, but using a root object name usually makes mappings and export structures more clear.
You could use HTTP to connect two systems so that Equvera CoNNeX TCP/IP Data Logger can listen on a TCP port and get JSON messages from an IoT gateway. Each HTTP request body contains a JSON object with sensor data:
POST /data HTTP/1.1 Host: logger.local Content-Type: application/json { "sensor":{ "id":"SENS01", "timestamp":"2026-01-02 08:00:00", "temperature":23.4, "humidity":45.8 } }
The logger captures the full HTTP request from a TCP/IP source. In the JSON Data Parser plugin, set Root object name to sensor . Enable Add parent name to value name if you want variable names like SENSOR.ID , SENSOR.TEMPERATURE , and SENSOR.HUMIDITY (along with Export names in uppercase).
In the JSON valueslist, define rules such as:
When a message arrives at 2026-01-02 08:00:00, the plugin can produce a set of parser items like:
DATE_TIME_STAMP = 2026-01-02 08:00:00 SENSOR.ID = "SENS01" SENSOR.TIMESTAMP = 2026-01-02 08:00:00 SENSOR.TEMPERATURE = 23.4 SENSOR.HUMIDITY = 45.8
These parser items can be forwarded to an SQL database using an export plugin. You can map DATE_TIME_STAMP to a timestamp column, SENSOR.IDto a device identifier column, and the temperature and humidity fields to numeric columns.
The JSON Data Parser plugin provides a controlled and efficient way to turn raw JSON streams into structured variables inside Equvera CoNNeX TCP/IP Data Logger, Equvera CoNNeX Data Logger Suite, and Data Logger Suite. It might help you get better at the data collection tasks you do in IoT and business areas.
The figure below shows how to select the plugin on the “Modules” page.
Fig.1. Selecting the plugin.
The figure below shows how to configure the plugin. Please, look at the documentation for the full description of all settings.
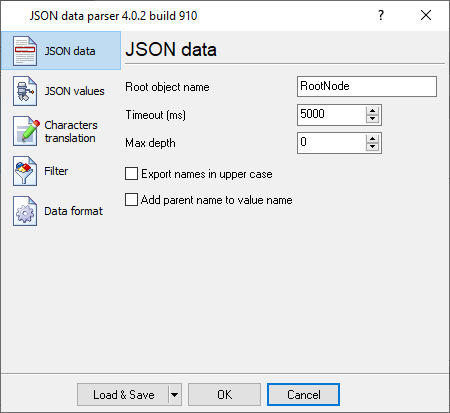
Fig.2. Configuring the plugin.
All plugins | ASCII Data Query and Parser | MODBUS RTU, MODBUS TCP, MODBUS ASCII | Scale Data Parser | DNP3 protocol | GE Fanuc Automation PLC (via CCM, SNP, SNP-X protocols) | Siemens SIMATIK PLC (S7-200, S7-300, S7-400, S5) | EtherNet/IP | M-Bus | Bacnet/IP | IEC 62056-21 | DLMS/COSEM | DL-T645-2007 | CJ/T 188-2004 | Kamstrup [KMP protocol] | Data parser module for ADAM, ICP-CON and NuDAM devices | RFC3164 (syslog protocol) data parser | HTTP data parser | File requests | XML Data Parser | CSV or delimited data parser | RFID Protocols Data Parser (LLRP, ISO 18000-6B, ISO 18000-6C) | JSON parser